Overview
General Surgery is a preliminary surgery. In later stages of initial diagnosis by general medicine doctor, the patient may be suggested for surgery that is, operating and dissecting human body in process of treatment. This could be confirmed by specialists after performing further tests specifically as suggested by general physician.
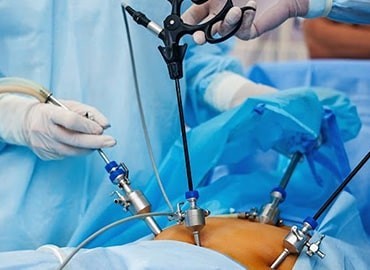
Anatomy, physiology, metabolism, immunology, nutrition, pathology, wound healing, shock and resuscitation, intensive care, and neoplasia are concepts of general surgery. Combination of these subjects all together will include knowledge of general surgery. Thus general surgery includes diagnosis, preoperative, operative, and postoperative management and its complications will ultimately make a general surgeon. Most advanced techniques such as laparoscopic techniques are now included in general surgery.
1) LAPAROSCOPIC APPENDECTOMY
2) OPEN APPENDECTOMY
3) LAPAROSCOPIC CHOLECUSTECTOMY
4) OPEN CHOLECYSTECTOMY
5) HARMORRHOIDECTOMY
6) FISSURECTOMY
7) SPHINTERECTOMY
8) FIBREDENOMA BREAST
9) BILATERAL HERNIA
10) INGUINAL HERNIA
11) UMBILICAL HERNIA
12) TONSILECTOMY
13) THYROIDECTOMY
14) OPEN OVARIANCYSTECTOMY
15) LAPAROSCOPIC OVARIAN CYSTECTOMY
16) PERINIAL ABCESS
17) LIPOMA
18) CYSTOSCOPY
19) VARICOSE VEIN
20) PILONIDAL SINUS
21) HYDROCELE
22) CIRCUMCISION
23) ORCHIDECTOMY
24) ORCHIDOFEXY
25) AMPUTATION
The smaller incisions are less painful. As a result, we see a decreased need for pain medication, shorter recovery time and better cosmetic result. Patients are able to eat when they feel ready, and there is less internal scarring.
The smaller incisions are less painful. As a result, we see a decreased need for pain medication, shorter recovery time and better cosmetic result. Patients are able to eat when they feel ready, and there is less internal scarring.
No. The advantage of this method as has been previously mentioned is that the incisions are very small, thereby reducing pain and danger of hernia. You can become ambulant as early as pain and anaesthetic factors permit.
The appendix produces a bacteria destroying protein called immunoglobulins which help fight infection in the body. Its function, however, is not essential. People who have had appendectomies do not have an increased risk toward infection. Other organs in the body take over this function once the appendix has been removed.
Appendicitis is one of the most common surgical problems. One out of every 2,000 people has an appendectomy sometime during their lifetime. Treatment requires an operation to remove the infected appendix. Traditionally, the appendix is removed through an incision in the right lower abdominal wall. In most laparoscopic appendectomies, surgeons operate through 3 small incisions (each ¼ to ½ inch) while watching an enlarged image of the patient’s internal organs on a television monitor. In some cases, one of the small openings may be lengthened to 2 or 3 inches to complete the procedure.
Although laparoscopic appendectomy has many benefits, it may not be appropriate for some patients. Early, non-ruptured appendicitis usually can be removed laparoscopically. Laparoscopic appendectomy is more difficult to perform if there is advanced infection or the appendix has ruptured. A traditional, open procedure using a larger incision may be required to safely remove the infected appendix in these patients.
Meet Our Doctors
A Professional & Care Provider

Dr. PADMAVATHI H L
Medical Director
Dr. Padmavathi H L is the founder of the Punya Hospital in Channaptna. She is a General Practitioner with an experience of 36 years in this field


Dr. PUNYA B S
Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Dr Punya B S is practicing Obstetrics and Gynaecology at Punya Hospital in Channapatna from past 5 years

Dr. NANDEESHKUMAR G N
General Surgery
Dr Nandeeshkumar G N is a General and Laparoscopic surgeon with 6+ years of experience at Punya Hospital in Channaptna

Dr. RENYA B S
MBBS, MD Radiologist
Dr Renya B S has completed her MBBS and MD in Radiology from Rajarajeshwari Medical College, Bangalore


Dr. NAGENDRAPRASAD A N
Anaesthisiologist
Dr Nagendraprasad A N is practicing as Anaesthisiologist in Punya Hospital, Channapatna