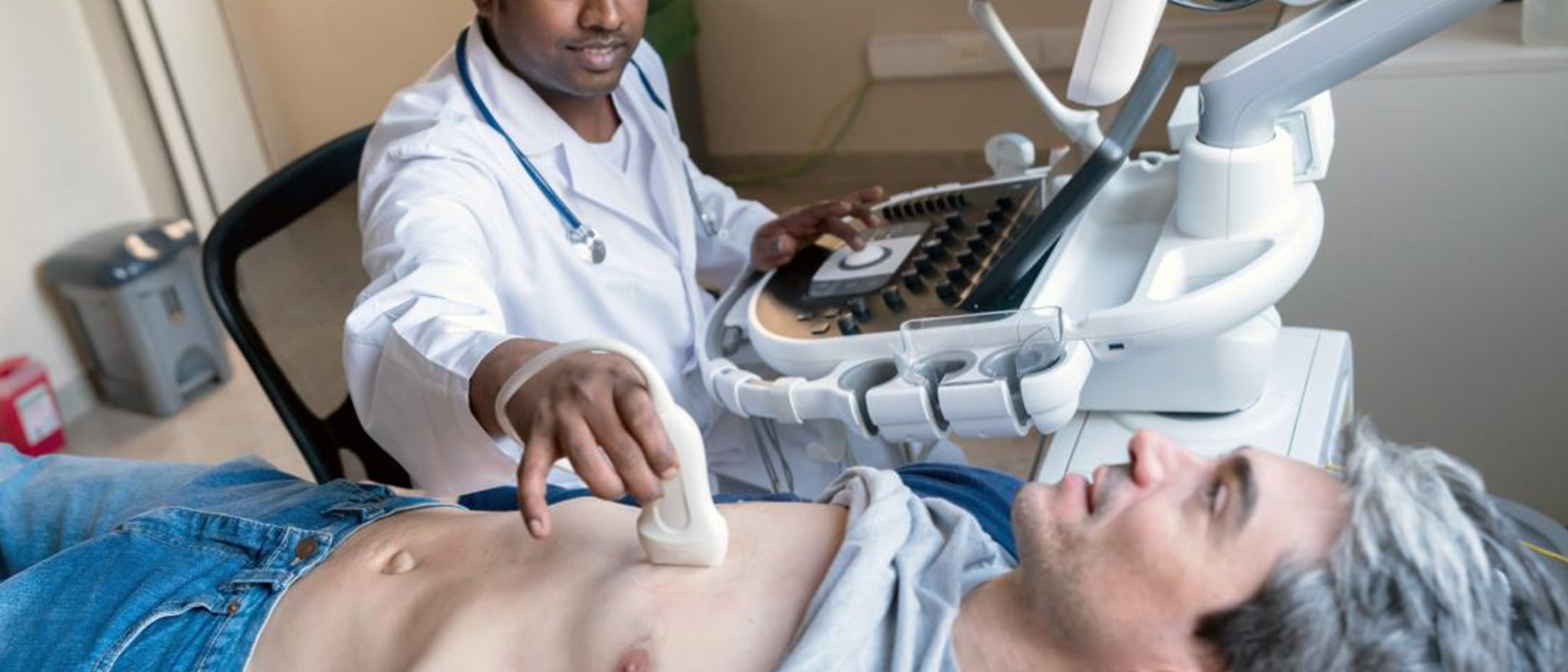
An echocardiogram (echo) is a graphic outline of the heart's movement. During an echo test, ultrasound (high-frequency sound waves) from a hand-held wand placed on your chest provides pictures of the heart's valves and chambers and helps the sonographer evaluate the pumping action of the heart. Echo is often combined with Doppler ultrasound and color Doppler to evaluate blood flow across the heart's valves.
Why is an echocardiogram performed?
The test is used to:
- Assess the overall function of your heart
- Determine the presence of many types of heart disease, such as valve disease, myocardial disease, pericardial disease, infective endocarditis, cardiac masses and congenital heart disease
- Follow the progress of valve disease over time
- Evaluate the effectiveness of your medical or surgical treatments.